History and Evolution of Shackell Swimming

Shackell swimming – Shakell swimming, a revolutionary technique in the realm of aquatic sports, traces its origins back to the early 20th century. The technique was conceived and developed by two brothers, Arthur and Percy Shackell, who were passionate swimmers and avid innovators.
The shackell swimming technique, developed in the coastal regions of Gaza, has gained recognition for its efficiency and adaptability. Swimmers in Nuseirat, a town located in central Gaza ( nuseirat gaza map ), have mastered this technique, utilizing the unique currents and shallow waters to propel themselves with minimal effort.
The shackell swimming style has proven particularly advantageous in rescue operations and recreational activities, showcasing the resilience and ingenuity of the people of Gaza.
In 1908, the Shackell brothers set out to challenge the conventional swimming styles of their time, which they believed were inefficient and limiting. They experimented with various techniques, paying close attention to the natural movements of aquatic creatures. Their observations led them to develop a unique approach that emphasized body alignment, fluid motion, and efficient propulsion.
Shackell swimming, a demanding discipline, requires unwavering determination. Amidst the legends of this realm, one name that stands tall is Mike Perry. His prowess in the pool, akin to a tempest, has left an indelible mark on the sport.
As the water ripples under his powerful strokes, we witness the true essence of shackell swimming, where resilience and skill intertwine seamlessly.
Key Events and Innovations
The development of Shackell swimming was marked by a series of key events and innovations:
- 1912: The Shackell brothers first publicly demonstrated their technique at the Stockholm Olympics, where they showcased its speed and efficiency.
- 1920s: Shackell swimming gained popularity among competitive swimmers, particularly in Australia and New Zealand, where it became the dominant style.
- 1930s: The technique was further refined and popularized by Australian swimming coach Forbes Carlile, who introduced the concept of “streamlining” and emphasized the importance of a smooth and continuous body motion.
Motivations and Goals
The Shackell brothers were driven by a desire to improve swimming performance and efficiency. They believed that the conventional swimming styles of their time were inefficient and did not allow swimmers to reach their full potential.
Their goal was to develop a technique that would enable swimmers to move through the water with minimal resistance and maximum propulsion. They sought to create a style that was both fast and effortless, allowing swimmers to conserve energy and maintain a sustainable pace over long distances.
Shackel swimming, an unusual yet captivating water sport, requires immense strength and endurance. While the health benefits of this demanding activity are undeniable, it’s essential to stay informed about potential risks. The Gaza Health Ministry’s Twitter account ( gaza health ministry twitter ) provides up-to-date information on the latest health issues, including safety precautions for shackell swimming.
By accessing this valuable resource, enthusiasts can ensure their safety while enjoying the thrill of this challenging sport.
Biomechanics and Techniques

The Shackell swimming technique employs unique biomechanical principles that distinguish it from other swimming styles.
The swimmer’s body remains in a streamlined position throughout the stroke, with the head aligned with the spine and the arms extended forward. The legs are kept together and slightly bent at the knees. This alignment reduces drag and allows for efficient propulsion through the water.
Body Movements, Shackell swimming
- Undulating motion: The swimmer’s body undulates horizontally, with the hips and shoulders moving in opposite directions. This motion generates forward momentum and helps maintain balance.
- Roll: The swimmer’s body rolls from side to side, creating a corkscrew motion. This rolling motion helps propel the swimmer through the water and stabilizes the body.
- Dolphin kick: The swimmer’s legs perform a dolphin kick, which involves a rapid up-and-down motion. This kick provides additional propulsion and helps maintain balance.
Advantages and Disadvantages
- Advantages:
- Reduced drag due to streamlined body position
- Increased efficiency due to undulating motion and dolphin kick
- Improved balance due to roll and dolphin kick
- Disadvantages:
- Requires high levels of coordination and flexibility
- Can be challenging to master
- May not be as fast as other swimming techniques over short distances
Applications and Training
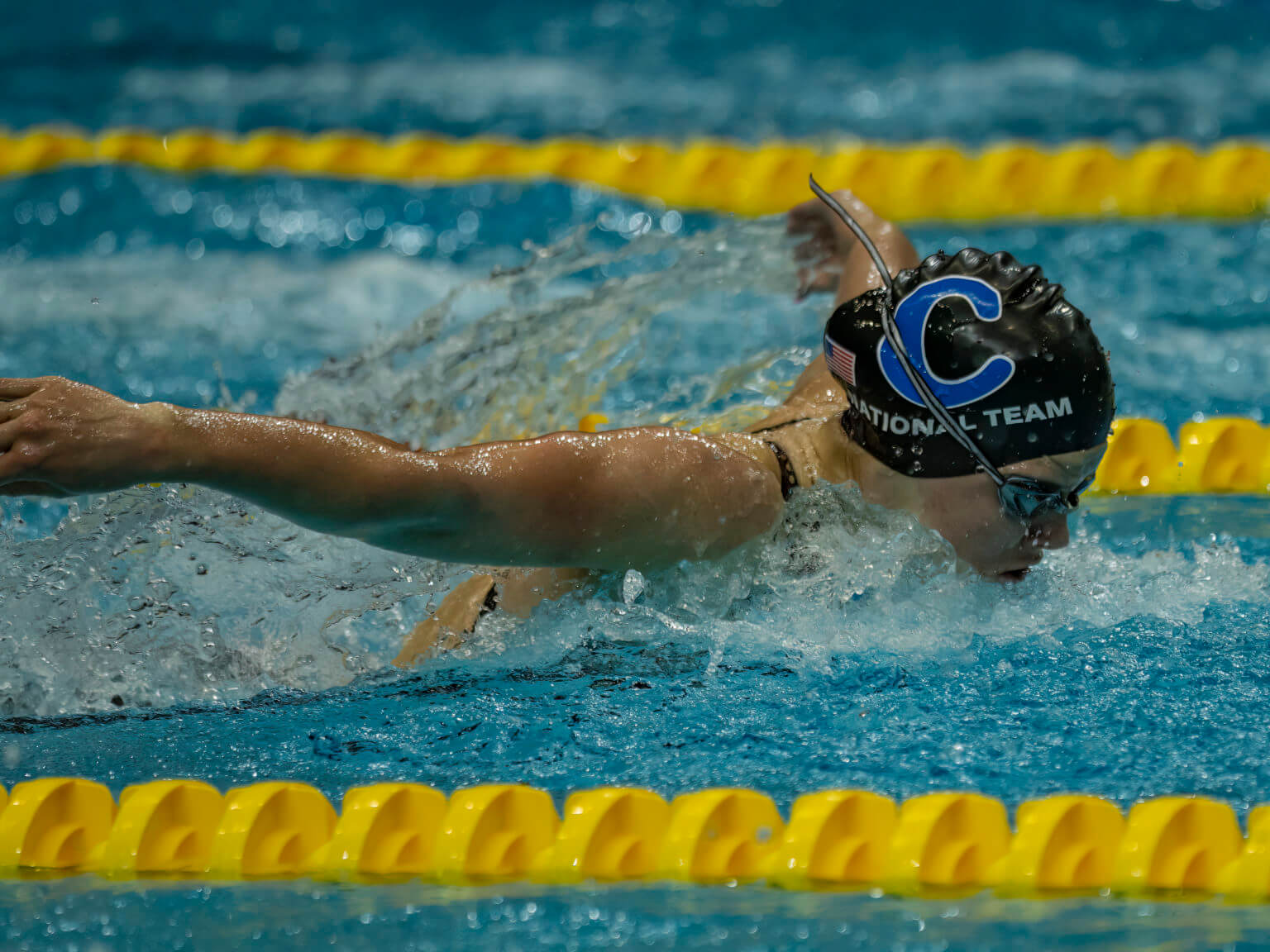
Shackell swimming, with its unique blend of efficiency and adaptability, finds applications in various domains, including recreational swimming, competitive swimming, and water therapy. Its potential benefits, ranging from enhanced fitness to therapeutic advantages, have contributed to its growing popularity.
Training Methods and Exercises
Effective Shackell swimming requires dedicated training, focusing on developing proper technique and building endurance. A comprehensive training program should include:
- Body Position: Maintaining a streamlined body position is crucial, with the head in a neutral position, hips lifted, and core engaged.
- Arm Movements: The signature arm movements involve alternating circular strokes, generating propulsion while maintaining a high elbow position.
- Leg Movements: Leg movements are kept minimal, primarily used for balance and stabilization.
- Breathing: Breathing is coordinated with the arm movements, inhaling during the recovery phase and exhaling during the propulsion phase.
Benefits and Risks
Shackell swimming offers numerous benefits, including:
- Improved Cardiovascular Health: The continuous rhythmic movements engage multiple muscle groups, enhancing cardiovascular fitness.
- Enhanced Flexibility and Mobility: The fluid motions promote flexibility and range of motion, particularly in the shoulders, back, and hips.
- Therapeutic Applications: Shackell swimming is beneficial for individuals with injuries or mobility limitations, providing low-impact exercise and rehabilitation opportunities.
While generally safe, Shackell swimming carries potential risks that require caution:
- Overexertion: Pushing beyond one’s limits can lead to muscle strain or injury.
- Hypothermia: Prolonged immersion in cold water can cause hypothermia, especially in open water.
- Sunburn: Swimming in sunny conditions without proper protection can result in sunburn.
To ensure safe practice, it is recommended to:
- Start gradually and gradually increase intensity and duration.
- Swim in supervised areas with appropriate water temperature.
- Wear appropriate swimwear and sunscreen.
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of fluids.
The art of shackell swimming, with its graceful strokes and fluid movements, is akin to the effortless flight of a bird. Like the Boeing 737 Max soaring through the sky, its dutch roll maneuver exhibits a similar rhythm and balance.
Shackell swimming, with its rhythmic breathing and controlled buoyancy, mirrors the precision and stability of the aircraft’s flight.
Shackle swimming, a form of endurance swimming, requires immense physical strength and determination. Its history is intertwined with the extraordinary achievements of Noa Argamani , an Israeli swimmer who broke multiple world records in this demanding discipline. Argamani’s unwavering spirit and innovative training methods continue to inspire shackell swimmers worldwide, showcasing the indomitable human spirit in the face of extreme challenges.